Voice of the Academician: Stem Cell Research and Prospects—The Magical Stem Cells: "Repairing People" Like Fixing a Car
来源:The Cellular Kingdom
2020-08-21
Humanity's journey extends far beyond the stars and the vastness of the ocean—indeed, even the mysteries within our own bodies remain far more complex than we currently understand. In this era of rapid advancement in human civilization and scientific technology, scientists are striving to manage the processes of life, aging, illness, and death—all starting at the cellular level. But what exactly is the underlying principle behind these groundbreaking efforts? And could humanity’s timeless dream of achieving immortality finally become a reality? To shed light on these questions, Academician Pei Gang from the Chinese Academy of Sciences provides an in-depth analysis, offering detailed insights into the discovery, current state, and future potential of stem cells.
As far as we currently know, all life on Earth—whether it’s humans, the diverse organisms in nature, animals, plants, or even the invisible microscopic world—is made up of cells. But how do these living entities reproduce, adapt, evolve, and ultimately give rise to the breathtakingly beautiful world we see around us? The answer lies within those countless tiny cells.
Within cells, there are also various types of cells—among them, one particular type stands out as exceptionally special, playing a critically important role. This cell can continuously divide, replicate itself, and constantly renew itself.
We call these cells—stem cells.
So, which types of cells have functions similar to those of stem cells?
Take humans as an example: both humans and animals rely on sperm and egg cells—biologically known as gametes—to reproduce. When sperm and egg unite, they form a fertilized egg, or zygote, which then begins an extraordinary process of unlimited cell division and specialization, gradually developing into an "embryo." Remarkably, all the diverse organs and functions in our body originate from that single, tiny fertilized egg. This is why the fertilized egg is considered a remarkably primitive type of cell—it holds the incredible potential to differentiate into virtually any tissue or organ in the adult organism. Cells with this unique ability to give rise to multiple cell types from a single initial cell are called stem cells.
It is clear that the easiest way to obtain stem cells is from embryos, which is why there is a specific type of cell known as embryonic stem cells—the earliest source of stem cells.
When "time travel" becomes reality
It is widely known that life is precious precisely because each person experiences it only once. On this one-way journey of life—from birth through growth, maturity, aging, and ultimately death—it’s an irreversible path, much like an arrow pointing forward. That’s why life is so invaluable. Our lives begin as stem cells, developing into fully formed individuals from a fertilized egg—a process that cannot be reversed. Yet scientists have long pondered this intriguing question: Could these cells somehow be "reversed"? Could they, like time travelers, transform back into more versatile, pluripotent cells—cells capable of becoming not just the specific types we see today, such as those in our hands, nose, eyes, or hair—but even more fundamental, primordial cells with the potential to differentiate into virtually any cell type in the body?
In 2006, Professor Shinya Yamanaka from Kyoto University in Japan conducted an experiment in which he used a set of proteins to reprogram an already differentiated cell back into a state with stem-cell-like potential. This remarkable reversal not only opened a new gateway for research across life sciences—such as cell biology and molecular biology—but also reignited hopes for humanity's ultimate aspirations: extending lifespan and achieving healthier, longer lives—themes that are deeply intertwined with the field of stem cells.
The findings from this experiment have expanded the potential applications of stem cells. When we fall ill—whether with conditions like stomach disorders, heart disease, high blood sugar, or hypertension—the underlying cause, in theory, stems from impaired stem cell function within our body or specific organs. By restoring and enhancing stem cell functionality, we may not only alleviate, treat, but even prevent these diseases from developing in the first place. This breakthrough opens up countless possibilities for improving human health.
"Artificial organs" tackle the challenge of organ transplantation
When we buy a car, it naturally ages over time, and its internal components gradually wear out or break down. Whenever damage occurs, we typically take the car to a repair shop—replacing a worn-out tire with a new one, swapping out a faulty water pump, and so on. Human health works in much the same way. As early as a century ago, surgeons pioneered "organ transplantation," a life-saving technique that has already given countless people a second chance at life. Yet today, the biggest challenge remains the severe shortage of available organs for transplant.
If cars are already manufactured by parts factories that supply components for replacement, could humans one day develop ways to produce the organs in our bodies that have aged, become unhealthy, or need replacing? That’s precisely what we now call organ engineering and tissue engineering.
△Image source: Internet
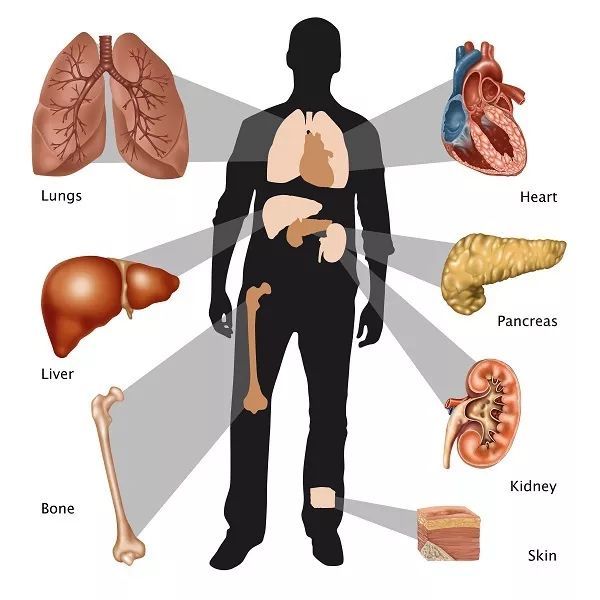
At this point, stem cells emerge as a particularly ideal material, since they are pluripotent cells capable of transforming—under the right conditions—into hepatocytes, renal cells, lung cells, cardiac cells, and more. Moreover, with the help of other biomaterials or specific environmental cues, these cells can even assemble into entire organs. Once a functional organ is fully formed, providing it with the necessary nutrients and support becomes straightforward, ensuring better health outcomes for humans and significantly enhancing our overall well-being.
Carrying forward Chinese civilization, stem cells hold great potential.
Everyone hopes to live a healthier life—yet, in reality, this depends on the quantity and quality of stem cells each person possesses. Over the past thousands of years, the Chinese nation has stood proudly among the world’s peoples, and we’ve cultivated an entire system of traditional Chinese medicine that has ensured our nation’s prosperity and vitality.
Traditional Chinese medicine encompasses a wide range of practices for health maintenance, wellness, and treatment—including the concept of "treating diseases before they occur." Surprisingly, many of these time-tested methods are now being linked to stem cells. Researchers have observed that several traditional Chinese herbs and medicines can actually boost the body’s own stem cells. This discovery opens up new avenues for reinterpreting both traditional Chinese medicine and even modern pharmaceutical approaches—offering a more effective and innovative way to enhance health and healing at the cellular level.
Stem cells are incredibly promising and represent a remarkably emerging field. Currently, countries around the world are investing significant amounts of human, financial, and material resources into stem cell research. In the future, stem cells are poised to have a profound impact on society, drive economic growth, enhance public health, and even reshape entire industries.
Science is continuously driving the advancement of human civilization.
In this cutting-edge field of life science, as with any other emerging technology, there are inevitably certain issues—some real, some possible, and others still largely potential—particularly ethical and moral concerns. That’s why humanity as a whole must remain vigilant, yet we shouldn’t let fear overshadow our ability to approach these advancements thoughtfully and responsibly.
For instance, gene-editing technology—currently a hot topic in the scientific community—is particularly significant because many diseases arise from genetic mutations or defects, and these conditions often have a hereditary component, posing a serious threat to the health of future generations. Thanks to gene-editing techniques, faulty genes can be precisely corrected. Combined with gene therapy or treatments that integrate stem cells, this approach holds the potential to transform and even reshape our lives as adults. However, if gene editing is applied directly to embryos, sperm, or eggs, it doesn’t just alter an individual’s life trajectory—it fundamentally rewrites the genetic makeup of all their descendants. In a sense, this means humanity itself could be reshaped for generations to come.
It’s just like artificial intelligence—on one hand, we’re investing heavily in research, while on the other, we’re worried that its rapid advancement might outpace humanity and even lead to it being controlled by the technology itself. The same goes for gene-editing technologies. So, how should we approach this?
First of all, let’s not fear science—science is one of the most important tools, methods, and means driving the advancement of human civilization. In fact, much of our civilization and culture is deeply intertwined with science. Therefore, we should proceed with full rationality, while operating within the bounds of societal-accepted moral and ethical principles.
China has been making remarkable strides in stem cell research, evolving rapidly from a modest research base just over a decade ago to now ranking second in the world. Over the years, we’ve achieved numerous groundbreaking milestones, inspiring hope and optimism across the nation. Looking ahead, the potential of stem cell technology continues to promise a brighter future—one where human lives are enriched and health is significantly improved!
Related News




