Mesoblast's Lesson: Can Chinese Stem-Cell Companies Rise to the Challenge?
2025-01-02
On December 18, 2024, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) officially approved Mesoblast’s bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) product, Ryoncil (remestemcel-L-rknd), for the treatment of steroid-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease (SR-aGVHD) in pediatric patients aged 2 months and older. This announcement has boosted morale across the entire stem cell industry, effectively dispelling the long-standing misconception that stem cells cannot be developed into effective therapies.
Stem cell drugs represent a new class of medications that go beyond traditional small-molecule therapies, featuring complex products with multiple active properties—and their journey to market has been fraught with significant challenges and uncertainties. In 2013, Mesoblast (founded in 2004), which had taken over the remestemcel program from Osiris (established in 1992), made a bold move to bring the drug to market, a process that ultimately took nearly 12 years. When combined with Osiris' earlier efforts in the Canadian and New Zealand markets, it actually took at least two full decades for bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell therapies to finally secure approval from the U.S. FDA.

01
Broaden your horizons—stay steadfastly on the path of those who have already succeeded.
Unlike the relatively well-established drug-likeness evaluation systems for existing drugs, MSCs pose significant challenges due to their dynamic nature, complex mechanisms of action, and the difficulty in monitoring them in vivo, resulting in low predictability of therapeutic efficacy and unclear modes of action. Consequently, in the development of MSC-based therapeutics, addressing critical issues such as the poor correlation between in vitro potency assays and clinical outcomes, as well as the inability of pharmacokinetic data to fully explain the underlying mechanisms of efficacy, remains a major hurdle before these products can reach the market.
In fact, Mesoblast has repeatedly encountered setbacks in this area as well. The company's first two clinical marketing applications submitted to the FDA were both rejected by the agency. In its responses, the FDA consistently raised concerns about efficacy assays and pharmaceutical issues. Despite Mesoblast having prepared comprehensive and compelling clinical trial data—primarily from studies such as Study 275, GVHD 001/002, and Study 280, which involved more than 500 patients across multiple countries and regions—and despite achieving remarkably positive clinical outcomes.
Mesoblast previously proposed that the mechanism of action (MOA) of its stem cells involves downregulating pro-inflammatory cytokines, boosting anti-inflammatory cytokines, and recruiting naturally occurring anti-inflammatory cells to the relevant tissues—thereby counteracting inflammatory processes linked to a variety of diseases.
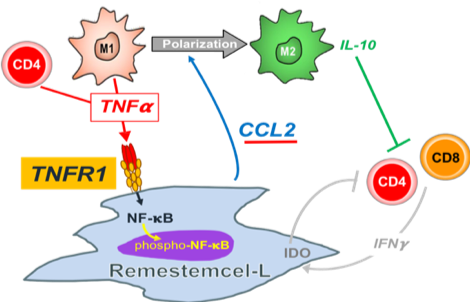
MSC exerts its immunosuppressive effects by mediating NF-κB activation via TNF-α, a mechanism that was validated using siRNA interference technology. Specifically, reducing or knocking out TNFR1 diminished the ability of MSCs to suppress lymphocyte activity, and varying levels of TNFR1 expression were found to correlate with the cells' immunosuppressive capacity. Based on these findings, Mesoblast has adopted TNFR1 as a key biomarker for releasing Remestemcel for clinical use—and in ongoing clinical trials, a clear correlation has been observed between TNFR1 expression levels and the therapeutic outcomes.
Stem cell-mediated repair of damage and immune modulation is an incredibly complex process. Identifying key biomarkers within this intricate mechanism, developing a rational model for the underlying action pathway, and establishing a clear causal link between the mechanism of action (MOA) and clinical outcomes—while ensuring these elements are both necessary and sufficient—are critical challenges that Chinese stem-cell-based pharmaceutical companies must address before submitting their New Drug Applications (NDAs).
02
Humbly open-minded, analyzing and assessing to identify areas for improvement
Dr. Peter Marks, Director of the FDA's Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER), stated: "The approval of Ryoncil marks a historic milestone in cell therapy, offering a groundbreaking treatment option for life-threatening conditions—particularly for pediatric patients who currently have limited therapeutic choices. This approval underscores the FDA's unwavering commitment to advancing innovative therapies that are both safe and effective, while significantly enhancing patients' quality of life."

This reflects the drug regulatory authorities' attitude toward innovative medicines—addressing unmet clinical needs. Perhaps we should put more thought into designing clinical protocols, avoiding mere trends or blind adherence. Instead, we should carefully select appropriate clinical strategies to effectively identify potential clinical benefits and the patient populations that could most benefit, thereby maximizing our chances of gaining support from the regulatory authorities.
Can China's stem-cell companies leverage Mesoblast's momentum to gain approval from the National Medical Products Administration? To find out, companies need to ask themselves several key questions: How do they stack up against industry standards in terms of process stability, clinical research, and pharmacodynamic studies? And most importantly, how much further do they still have to go on this challenging journey?
First, regarding process stability, have the appropriate critical quality attributes been identified? And is it possible to achieve scalable production of stem cell products?
Second, in terms of clinical research, has an appropriate clinical strategy been developed? Is there a sound clinical study design in place? And will robust clinical support data be available?
Once again, regarding the pharmacological studies—does the proposed mechanism of action hold up under scrutiny? Have suitable pharmacodynamic markers been identified, and can they be validated by clinical data?
03
Innovation leads the way, driving the future development of the industry.
As a leading pioneer in the stem-cell pharmaceutical industry, Jiuzhitang Maker (Beijing) Cell Technology Co., Ltd. (hereafter referred to as Jiuzhitang Maker) has remained steadfastly committed to advancing China’s journey toward stem-cell-based drug development. With an unwavering dedication to innovation and excellence, the company continues to push the boundaries of scientific advancement and deliver unparalleled quality in its cutting-edge solutions.

Jiuzhitang Maker deeply understands that manufacturing processes directly impact therapeutic efficacy, clinical progress, and even future business models. Building on Stemedica’s pioneering stem cell technology in the U.S., Jiuzhitang Maker has continuously innovated and pushed beyond its own limits, establishing its unique core competitiveness: a specialized hypoxic culture process coupled with world-class, large-scale expansion capabilities. This breakthrough addresses the critical bottlenecks hindering industry growth. Currently, Jiuzhitang Maker boasts the capacity to produce 10 million finished doses—each containing 50 million cells—from a single bone marrow source. With over 100 batches of stem cell products already successfully manufactured, the company has achieved exceptional batch-to-batch consistency in its mesenchymal stem cell products.
For stem-cell pharmaceutical companies, drug quality is like the cornerstone of a towering skyscraper—it is the very foundation upon which the company’s survival and growth depend. Jiuzhitang Maker has always regarded cell quality as its lifeline, building a robust quality management system and standardized quality-control protocols (covering identification, potency, safety, purity, and formulation) firmly rooted in advanced manufacturing processes. The company recently submitted four distinct human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell banks—along with their corresponding formulations, raw materials, and high-passage products—for a total of 16 samples—to the China National Institute for Food and Drug Control for re-examination. All test results came back fully compliant. This confirms that Jiuzhitang Maker’s “human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell” products have met the stringent national standards for clinical application in terms of essential biological characteristics, microbiological safety, biological safety, and therapeutic efficacy.
Jiuzhitang Maker is fully leveraging its role as a pioneering enterprise, drawing on its core expertise in stem cell-based new drug development—specifically its capabilities in process development, scalable manufacturing, and quality control & testing services. The company has established the Stem Cell CQDMO (Contract Quality, Development, and Manufacturing Organization) service platform, offering industry players and research institutions a comprehensive, end-to-end CQDMO solution. This includes services such as stem cell library establishment, process development, methodological development and validation, as well as regulatory submissions. By doing so, Jiuzhitang Maker helps stem cell-related companies—from early-stage R&D and investigator-initiated clinical trials (IITs) through to Investigational New Drug (IND) applications and commercial-scale production—efficiently advance their pipeline of stem cell-based therapies toward both clinical advancement and market launch.
"Great buildings rise from the ground, brick by brick—every single one is essential to the foundation." Pharmaceutical production cannot rely on shortcuts or guesswork; it certainly can’t be done in isolation. Jiuzhitang Maker aims to leverage its CQDMO service platform to provide stem-cell companies not only with GMP-compliant facilities that meet both Chinese and U.S. regulatory requirements, but also with a dedicated team of experts and a robust quality management system. Drawing on its own extensive experience, Jiuzhitang Maker will offer invaluable guidance—ranging from developing tailored production strategies and refining quality-control methodologies to preparing comprehensive registration dossiers. Together with industry peers, we’re committed to advancing collaboration, fostering mutual success, and collectively driving the growth and innovation of China’s stem-cell sector.
Related News




