Details
Commonly known as apoplexy, cerebral stroke is the second most common cause of death and disability in the world. Stroke is the most common cerebrovascular disease causing high disability rate and mortality rates. The incidence rate varies greatly in different regions of the world and is closely related with diet and living habits. In recent years, the overall incidence rate has increased year by year. China is a country with high incidence of stroke. Results of the third survey on death causes published in 2008 show that cerebrovascular disease has risen to the first place among various causes, and there has been an increasing number of young-age patients: 10% to 15% of young and middle-aged patients develop symptoms before 45, and it is hard for stroke patients to restore health.
About 70% to 80% stroke survivors are unable to work independently to some degrees, and those with severe disability account for more than 40% with an recurrence rate of 41%. There are currently no clinically effective drugs except rehabilitation treatment. In recent years, the huge development potential existing in the stem cell industry has attracted many researchers to invest in stem cell therapies for stroke. A large number of experimental studies on animal models of stroke have also shown that stem cell treatment has a good effect on stroke. There are 63 clinical studies using stem cell therapy for stroke registered in the US clinical trial website (clinicaltrials.gov), as shown in the figure, including 20 in the US, 16 in Europe, and 16 in Central Asia (14 in China, 2 in South Korea).
A phase II clinical trial using ischemic-tolerant human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (itMSCs) therapy sponsored by Stemedica has been completed. The inclusion criteria are clinical diagnosis of stroke for more than 6 months, and an NIHSS score of 6-20. The patient has shown no significant improvement for two months before enrollment.
On January 11, 2019, Stemedica announced the positive results of its Phase I/IIa clinical study of allogeneic stem cell therapy for ischemic stroke in the United States. In a multi-center, open-label Phase I/IIa study, ischemic tolerant mesenchymal stem cells (itMSCs) achieved safety, tolerability, and preliminary efficacy objectives. The data demonstrated that itMSCs administered intravenously appeared to be safe and well tolerated. No serious adverse events or clinically significant changes in lab and imaging measurements were reported. Results of the study are supportive of advancing the clinical program. Following a meeting with the FDA anticipated in the first half of 2019, Stemedica plans to initiate a Phase IIb trial. Detailed safety data and clinical results from the Phase I/IIa study with itMSCs will be published and presented at a future medical conference.
The news release can be accessed at http://www.stemedica.com/stemedica-cell-technologies-reports-positive-data-in-phase-i-iia-study-of-allogeneic-stem-cells-for-ischemic-stroke/
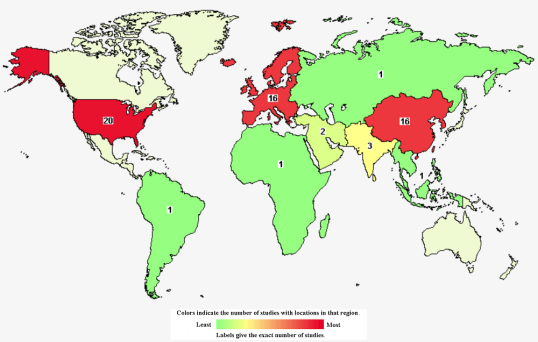
Distribution of worldwide clinical studies treating stroke with stem cells